Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Table of Contents:
In the world of information and technology, safety and security have become the topmost priority in every aspect of our daily lives. From personal information to financial transactions, we trust the intermediaries to protect our data and transactions. Yet, traditional systems are vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and errors. Welcome to the Blockchain, a revolutionary technology that promises decentralized data, provides security, and makes it virtually tamper-proof. Blockchain spreads control across a network, ensuring that every transaction is recorded transparently. In this blog, we will explore what sets Blockchain apart from the conventional method we used to know and why Blockchain is rapidly evolving in this decentralized world.
Blockchain is the decentralized, digital ledger technology that records transactions across the network of computers in a secure, transparent, and immutable way. Each transaction is recorded into a “block” (A block in the Blockchain is a digital record that contains a collection of data, a list of transactions), which is linked to the previous block, forming a continuous “chain.” It ensures that your data cannot be altered or deleted. Unlike the conventional way, Blockchain relies on a distributed network where every participant (node) has access to the same information, fostering trust and transparency.
Now let’s get to know about the key components of Blockchain.
1. Blocks: The basic units that store data, such as transaction records, and are linked together in chronological order.
2. Nodes: Independent computers within the blockchain network that maintain copies of the ledger, validate transactions, and communicate with each other to reach consensus.
3. Hash: A cryptographic signature unique to each block, ensuring data integrity. Each block also contains the hash of the previous block, linking them together.
4. Consensus Mechanism: The process by which nodes agree on the validity of transactions, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain. Common methods include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
5. Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enabling automated and trustless transactions.
6. Distributed Ledger: A decentralized, shared ledger where all participants have access to the same data, promoting transparency and reducing the need for intermediaries.
But you might wonder how Blockchain works. What is the actual process?
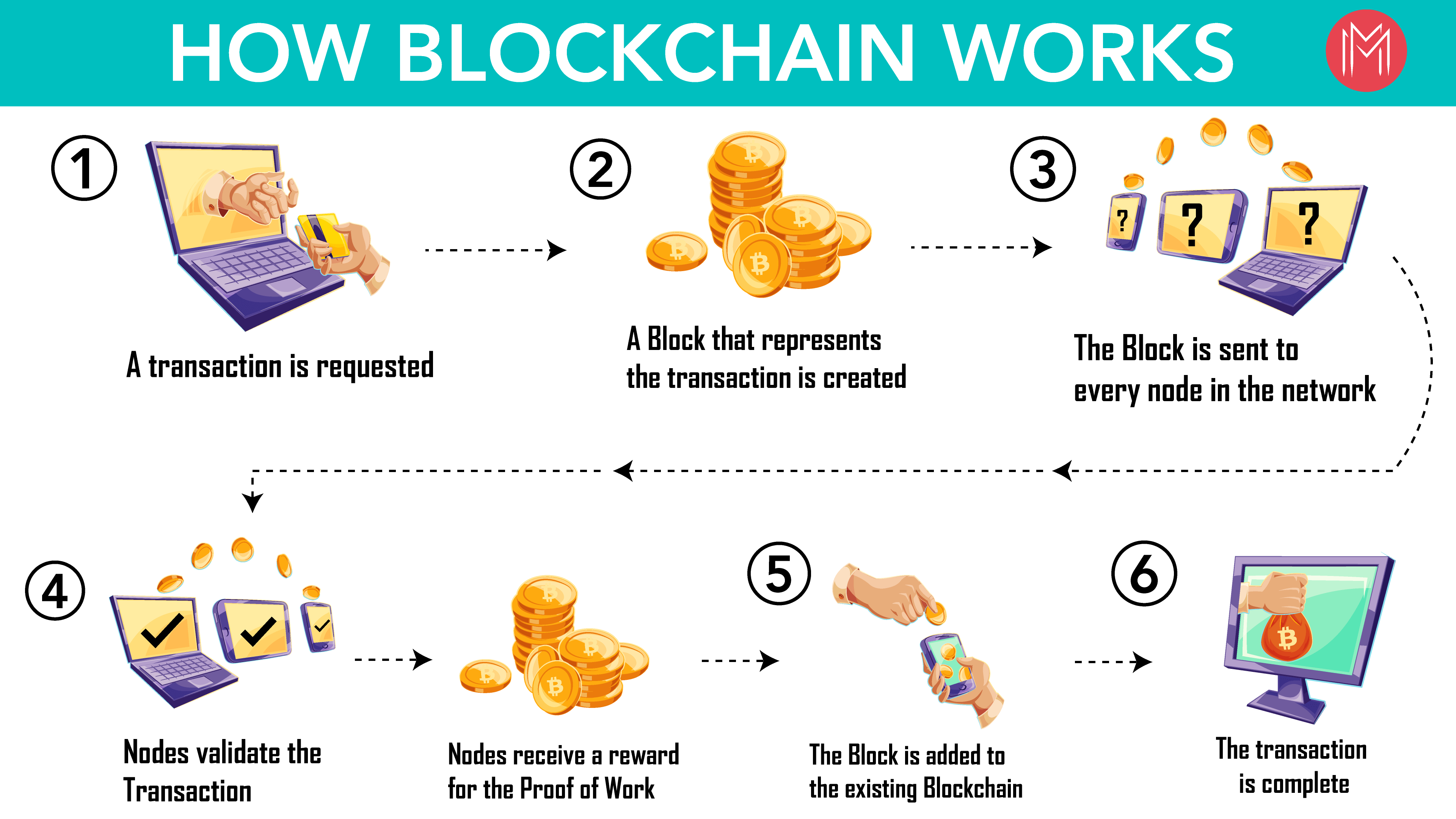
Source: Mindmajix
The transaction occurs when any user wants to transfer assets (be it cryptocurrency, data, or any other digital good). It could be a straightforward payment in the case of Bitcoin or a highly complex operation that involves smart contracts. The transaction includes information about the sender, receiver, and amount, along with a digital signature that authenticates the identity of the user.
Once a transaction is started, it is sent to a network of nodes or computers in the blockchain. Every node in the network receives the transaction request and verifies its authenticity by checking if the user has the right to perform this transaction.
Nodes validate the transaction by verifying the user’s digital signature and ensuring that all transaction conditions are met (such as checking if the funds are available).
Proof of Work (PoW): Miners (nodes) compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. The first miner to solve it gets to add the block and is rewarded with cryptocurrency.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are selected to create new blocks based on the number of coins they “stake” in the network, with fewer energy requirements compared to PoW.
Once confirmed, the transaction is grouped with other transactions that occurred around the same time into a block. A block contains several different elements –
A hash of the previous block, linking it to the prior block, creates a sequence of blocks-thus the name “Blockchain”.
Once the block is verified by the network through the consensus mechanism, it is added to the existing blockchain, becoming a permanent part of the ledger. The chain of blocks is stored across the distributed network of nodes, and all nodes update their copy of the blockchain to include the newly added block.
After a block is added to the blockchain, its data may never be altered or deleted without affecting every block afterward. Because each block is secured by its hash and the hash of the block that it follows, if a person wants to alter a block, the hash would change, breaking the link to the block after it and signaling to the network that something was amiss. This immutability makes blockchain very secure and resistant to fraud or manipulation.
Once the block is appended to the chain, that transaction is finally complete and confirmed. The data is visible and accessible to nodes across the network. Depending on the blockchain, the transaction confirmation may require multiple blocks to be added after the current one to ensure security (for example, Bitcoin requires six blocks for full confirmation).
But why would you use Blockchain technology? Why Blockchain is so unique?
Blockchain does not require any central authority because it scatters data across a network of nodes. Decentralization decreases dependence on third-party intermediary organizations such as banks or any other system for verification; because of that reason, it reduces the cost of transactions and enhances processes to work efficiently.
Blockchain uses advanced cryptography, and recorded data in the block cannot be altered, it would be linked to the prior block, hence it is impossible to alter or change information by hackers. Blockchain ensures that transactions are safe and of integrity.
All the participants of a blockchain system have access to the same data, which is verifiable. The transparency of the blockchain ledger fosters trust among participants because transactions are easily auditable and traceable, reducing the risk of fraud.
Traditional systems rely on the intermediary which causes the transactions to take more time. Blockchain technology automatically executes smart contracts and removes vast processes by determining the conditions when they are fulfilled for self-execution as payments, transfer of assets, and settling contracts.
Removing the intermediary in blockchain and automated verification, auditing, and record-keeping saves costs related to operations. Be it financial services, supply chains, or health care; organizations can cut transaction fees as well as labor-intensive processes.
There are various types of Blockchain. Public Blockchain, Private Blockchain, Consortium Blockchain, Hybrid Blockchain.
Source: academy.moralis.io
| Feature | Public Blockchains | Private Blockchains |
| Access | Open to anyone to join and participate | Restricted access, typically within an organization |
| Authority | Decentralized, no single entity controls the network | Centralized, controlled by one organization |
| Consensus Mechanism | Uses mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) | Can use customized, permission consensus mechanisms |
| Transparency | Fully transparent, all transactions are visible to the public | Transactions are visible only to authorized users |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Hyperledger, Corda |
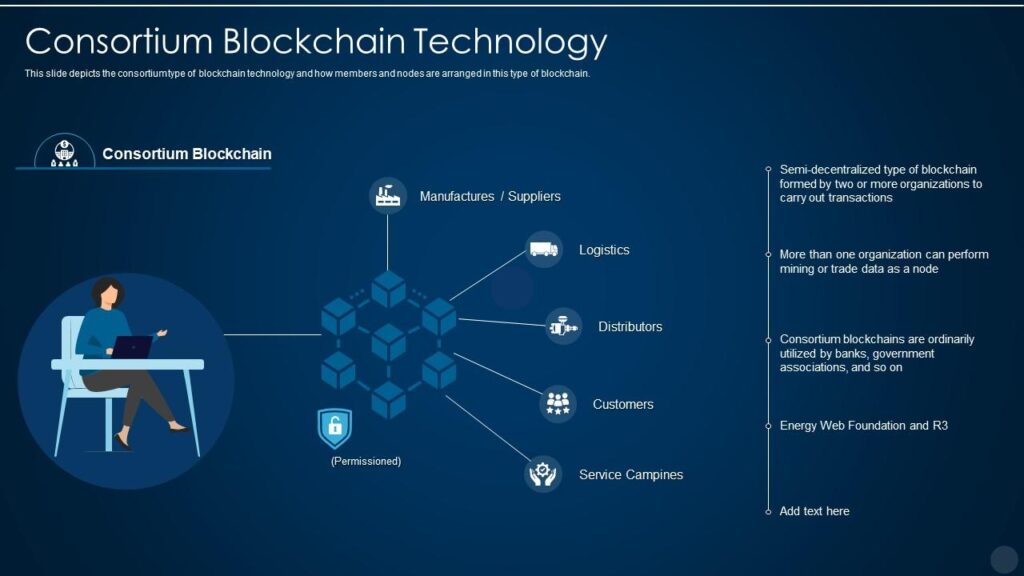
Source: slideteam.net
A Consortium Blockchain, known as Federated Blockchain, is a semi-decentralized network, where the blockchain is managed by a group of organizations or institutions rather than a single entity. Unlike, public blockchains, which are fully decentralized, and private blockchains, controlled by only one organization, consortium blockchains offer this middle-ground approach with a selective decentralization model.
Example: R3 (used in banking), Energy Web (used in the energy sector).

Source: slideteam.net
A hybrid blockchain combines the features of public and private blockchains. It offers a flexible solution that allows for both open and closed systems. While some parts of data may be public in a hybrid blockchain, the other parts remain private or accessible only to chosen participants. With such capability, organizations can control access to sensitive information while taking advantage of the transparency and security provided by blockchain technology.
Example: Dragonchain, XinFin.
There are various types of applications of Blockchain technology. Let’s get to know about them.

Source: hyperhci.com
Blockchain is transforming the finance form with efficient, transparent, and secure platforms.
Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, support decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
Smart Contracts: Smart Contracts will automate agreements and enforce compliance on both sides, without intermediaries, for example: loans or insurance.
Cross-border payments: Cross-border payments became faster and cheaper, and intermediaries such as banks were no more required.
DeFi: DeFi is short for Decentralized Finance. It means decentralized financial services that give access to lending, borrowing, and trading without central authorities.
Source: techment.com
While controlling and efficiently working with the supply chains, Blockchain technology also affords a higher level of operational transparency and traceability.
Traceability: Each and every step undergone from preparing such product for sale e.g. in the food or pharmaceutical industries can be stored and verified on the blockchain network.
Fraud Management: There is no way of keeping back or altering any record on the chain and therefore such enables risk or chance of fraudulent activities to an extent.
Smart Contracts: Entering supply or service agreements with the respective suppliers is a straightforward process that rarely has delays or disagreements.
Environmental Impact: Blockchain can facilitate the assessment and evidence of these kinds of ethical considerations and their practice – e.g. fair trade or organic certification.

Source: blockchainappsdeveloper.com
With the rise of blockchain technology, healthcare management can also be more efficient in the management of patient data privacy and research.
Security of Patients’ Medical Data: Patients can share and control their medical data across different health providers while reducing the risk of duplicity and mistakes.
Pharmaceutical Chain Improvement: The potential of blockchain can be fully realized in tracking all manufacturers and patients of a given drug and hence include the fight against fake pharmaceuticals.
Clinical Studies: Blockchain allows for the preservation of sensitive results from research in clinical trials.
Sharing of Datasets: Blockchain may enable the controlled and secure sharing of linked de-identified patient data for the purpose of conducting clinical research.
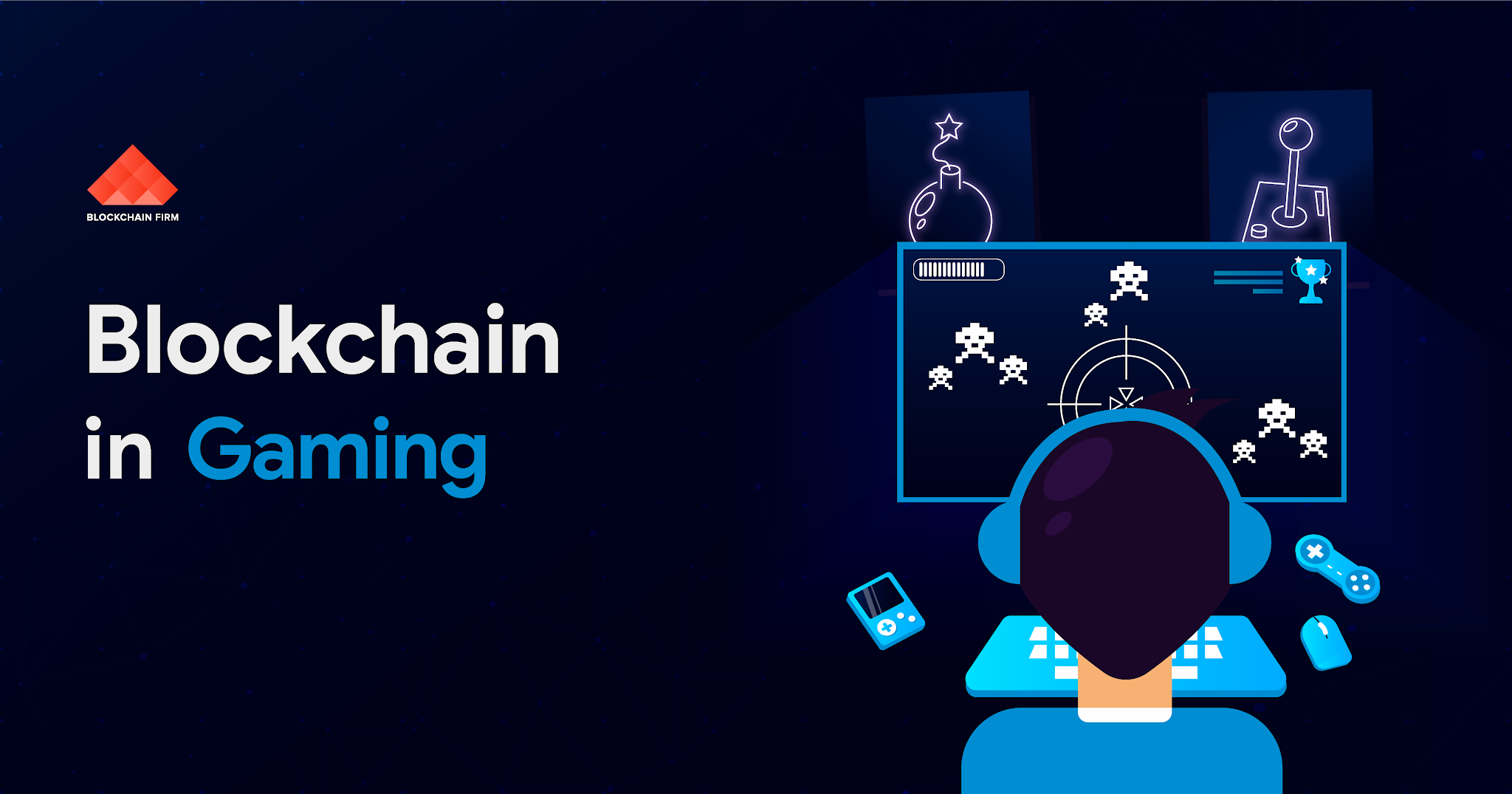
Source: in.pinterest.com
The advent of blockchain technology has come with digital property, distributed economies, and enriching play experiences that are revolutionizing gaming.
In-game Assets: Players can now buy, sell, or trade much-loved in-game characters, clothes, weapons, and skins as NFTs.
Play to earn: Players have a chance to earn some cryptocurrency or tokens by engaging in such games adding another layer of economic value.
Decentralized gaming: Games developed on the blockchain are more transparent, allowing for fewer unfair advantages and the ability to restrain the players.
Asset portability: One of the features of blockchain is it allows the assets to be used in more than one game or application by the same player.
The emergence of blockchain technology has taken the world by storm especially due to its use in cryptocurrencies. These unique networks have changed the way transactions, contracts, and assets are handled by providing a high degree of safety and eliminating the need for middlemen. Now, let’s try to highlight several essential blockchains and explain how these blockchains support various cryptocurrencies.

Source: lens.monash.edu
Bitcoin’s blockchain, created in 2009 by the elusive Satoshi Nakamoto, is the earliest and the most famous of them all. It is the backbone of Bitcoin, the digital currency that started it all. The blockchain underpinning Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW), where participants known as miners help validate transactions and keep the network secure by solving puzzles that involve cryptographic hashes.
Due to its robustness and its dispersed nature, it is no wonder that even with the emergence of many other digital currencies, bitcoin remains the most prestigious and highly valued of them all. However, the issue of its scalability and how fast transactions are processed has always been a matter of contention.

Source: tarlogic.com
Ethereum, proposed in 2015 by the self-described geek Vitalik Buterin, is more than just an electronic currency. The Users can freely serve the ETH cryptocurrency, which is the default currency for Ethereum, but this is not what ETH is about. What makes Ethereum so different from the other blockchains is the smart contracts feature that simply allows the Ethereum blockchain to create contracts that are executed as codes on the blockchain. This allowed the emergence of dApps and many more uses including DeFi and NFTs.
While Ethereum started by using Proof of Work consensus, it is now based on the Proof of Stake consensus of Ethereum 2.0 in order to solve the issues of scalability and environmental impact.

Source: en.cryptonomist.ch
As launched by Justin Sun in 2017, Tron has adapted cryptocurrency technology to allow the free creation of content without the censorship threats on the creators. Thus, the platform focuses on high transaction speeds and the growing number of dApps available a majority are in the content sharing and entertainment sector.
Tron works under the Dpos model which is cost-effective and timesaving as transactions can be completed in a matter of seconds without costing much, that is why it is widely used in several mobile applications where content is shared, hosted, and played, games and social networks. TRX is the main token used in the TRON network and it is aimed at removing intermediaries allowing content creators to be rewarded directly.

Source: 0xdev.co
Launched in 2020 by Anatoly Yakovenko, Solana Blockchain is popular for its incredible speed and low transaction cost, making it one of the fastest blockchains in its entire history. By utilizing a blend of proof of stake and a unique system of proof of history, Solana is capable of processing thousands of transactions in a matter of seconds which solves the scalability challenges many of the traditional blockchain networks face. This makes Solana especially suitable for DeFi, gaming, and NFT projects. Its coin SOL plays an important role in securing the network and staking.

Source: Quartz
This is a process of the Bitcoin Blockchain which is known as the Bitcoin Cash Blockchain. Bitcoin Cash (BCH) on the other hand came into existence in the year of 2017, which was a fork that addressed the issue of Bitcoin’s scalability issues by increasing the block size limit. This allows Bitcoin Cash to accommodate more transactions within a single block, thus making cheaper and faster transactions as opposed to Bitcoin.
Even though they both share the same basic tenets of being decentralized and providing security, Bitcoin Cash is more precise for daily transactions considering its speed and low charges, even though most people do not use it as much as they do with Bitcoin.

Source: defipedia.com
WAX Blockchain was launched in the year two thousand seventeen, it has gained popularity among gamers and NFTs because it is an eco-friendly, energy-saving Proof of Stake model. WAX (Worldwide Asset eXchange) is a blockchain focused on virtual and digital assets, particularly when it comes to games and NFTs. It is now possible for users to create, purchase, rent, or trade virtual items such as NFTs with very low costs of operations. There is also an easy dev interface, and the platform has collaborations with world-known gaming and entertainment companies. The ecosystem is powered by WAXP cryptocurrency which is used for staking, governance, and transactions.
However, with developments in technology, Blockchain has expanded its scope to even further technologies. There are new things to explore for investors whereby blockchain introduces means to enhance one’s investments and it portrays the future of human beings. Investments in blockchain might take so many forms and two of them are Blockchain ETFs and Blockchain Certifications.

As an alternative, Blockchain Exchange Traded Funds will allow investors to access blockchain-related industries without buying volumes of cryptocurrencies concentrating on a particular one. These funds purchase stock in firms working on the blockchain, from manufacturers of the components to companies that create applications that run on blockchain technology.
Example: Technology companies like IBM or financial service firms like Square. By holding shares in blockchain ETFs, investors can indirectly gain from the growth of blockchain applications without the volatility associated with direct cryptocurrency investments.

Source: Software Testing help
As blockchain’s influence grows, so does the need for expertise in the field. Blockchain certification programs offer a direct investment in knowledge, enabling professionals to capitalize on the expanding job market for blockchain developers, analysts, and consultants. Programs like the Certified Blockchain Professional (CBP) or Certified Blockchain Developer (CBD) provide industry-recognized credentials that signal expertise to employers. These certifications not only boost individual career prospects but also make professionals critical contributors to blockchain’s continued evolution, providing a solid investment in long-term success.
Over recent years, Blockchain has undergone numerous changes and improvements. Blockchain platforms and applications spreading across almost all industries. These changes are altering the perception of decentralized systems and are leading to the adoption of blockchains in activities other than cryptocurrencies. Below are some exciting blockchain technologies and trends to watch out for.

Source: watcher.guru
Riot Blockchain is one of the biggest Bitcoin mining companies in the USA. It mainly focuses on its mining operations and aims to enhance the infrastructure for Bitcoin by developing symbiotic large-scale mining operations. To improve mining capability and secure and decentralize the Bitcoin network as a whole, Riot employs state-of-the-art mining equipment and energy-efficient technology. With the rise in the popularity of cryptocurrency mining, this business sector must hopefully lead innovation, growth, and expansion of operations for Riot Blockchain.

Source: steempeak.com
Hive Blockchain combines cryptocurrency mining with a green energy approach, focusing on mining Bitcoin and Ethereum using renewable energy. With data centers in countries like Sweden and Iceland, Hive aims to operate sustainably by reducing carbon footprints in the energy-intensive mining process. By aligning with eco-friendly initiatives, Hive Blockchain is carving a niche in the mining industry while contributing to environmentally conscious blockchain practices.

Source: argoblockchain.com
Cryptocurrency mining has also become popular among other industries, so Argo Blockchain’s differences are not only in this it. Its focus is on energy-efficient mining. Based in the United Kingdom, Argo has several huge mining farms throughout the world but concentrates on climate change mitigation. With this agenda, Argo aims to lead the blockchain mining sector and be described as innovative, transparent, and environmentally responsible. So, this corporation is also diversifying its activities by researching technologies such as non-Bitcoin cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (deFi) alongside blockchain.

Source: coingecko.com
Flow Blockchain is designed with NFTs, games, and decentralized applications in mind. Flow was developed by Dapper Labs, the guys behind CryptoKitties, and this is a fast, developer-centric blockchain that overcomes many of the scaling problems typical of other blockchains. Flow’s unique architecture allows for a high transaction throughput, while still maintaining a level of decentralization which is perfect for use in applications such as NBA Top Shot and other entertainment-orientated applications. Because of its emphasis on usability and scaling, this is one of the most advanced blockchains for gaming, digital assets, and consumer-orientated dApps.
Blockchain technology is transforming industries across the globe, and understanding the tools and resources available can help you navigate this new digital frontier. Whether you’re managing cryptocurrency, tracking transactions, or deep diving into the technology behind a project, the following tools can be invaluable.
Blockchain wallets are digital tools that allow users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies securely. These wallets come in various forms, including hot wallets (connected to the internet, like mobile or desktop apps) and cold wallets (offline, such as hardware devices). They ensure that only the wallet owner can access the private keys necessary to authorize transactions. Popular wallets like MetaMask and Ledger not only provide secure storage but also allow interaction with decentralized applications (dApps), enabling users to engage in various blockchain activities.
A blockchain explorer is a tool that functions like a search engine for the blockchain network and its activity and displays information on various transactions, blocks, and addresses. Such tools allow for a very quick degree of transparency as users can observe the transactions being made or even the specific money being used in a particular transaction.
An example, Explorers like Etherscan (for Ethereum) and Blockchain.info (for Bitcoin) are widely used to monitor network activity, confirm transactions, and even audit smart contracts. They are essential for anyone involved in blockchain, as they offer a detailed look into the functioning of a blockchain.
A blockchain whitepaper is a detailed document that outlines the technical and business aspects of a blockchain project. It’s often the first introduction to a new cryptocurrency or decentralized solution, offering potential investors or developers a deep dive into its mechanics, use case, and potential market impact.
The Bitcoin whitepaper, written by Satoshi Nakamoto, is one of the most famous examples, setting the stage for the entire cryptocurrency movement. Whitepapers help users understand the innovation and problem-solving approach behind blockchain projects, making them key resources for evaluating new opportunities.
Blockchain technology, once synonymous only with cryptocurrencies, is rapidly expanding into various industries, promising to reshape how we conduct business, share data, and build trust. As we look to the future, blockchain’s evolution presents both exciting opportunities and notable challenges. Below is a glimpse into the trends, predictions, and hurdles that will shape its path forward.
DeFi is expected to grow, offering decentralized financial services that eliminate intermediaries like banks. With lending, borrowing, and staking becoming more user-friendly, DeFi could democratize access to financial tools globally.
More corporations are expected to adopt private and consortium blockchains for internal use. Sectors like supply chain management, healthcare, and finance will use blockchain for secure data sharing and operational transparency.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are evolving beyond collectibles into real-world applications, such as tokenized assets in real estate or intellectual property. NFTs could expand into digital rights management or even personal identity verification.
One significant trend is the focus on cross-chain interoperability, where different blockchain networks communicate seamlessly. This will help reduce the fragmentation of ecosystems and enable more fluid transactions across networks.
Countries are exploring CBDCs—blockchain-based versions of national currencies. Governments will likely use blockchain to improve the transparency and efficiency of their financial systems, with CBDC projects emerging from countries like China, the EU, and the US.
As blockchain networks grow, ensuring they can handle large volumes of transactions efficiently remains a significant challenge. Layer 2 solutions like rollups, sharding, and sidechains are emerging to improve scalability, but widespread implementation will take time.
The high energy consumption of blockchain networks, especially those based on Proof of Work (like Bitcoin), poses environmental concerns. Shifting to more eco-friendly models such as Proof of Stake and adopting green blockchain initiatives will be crucial.
Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate blockchain without stifling innovation. Clear regulations that protect users and encourage innovation could unlock more blockchain adoption, while restrictive rules may slow progress.
While blockchain is secure by design, hacks of decentralized applications and exchanges are not uncommon. Building more robust security frameworks and educating users will be essential for reducing risks in the decentralized space.
Beyond digital currencies, blockchain presents a massive opportunity in asset tokenization, where real-world assets like real estate, commodities, or art are represented as digital tokens. This could revolutionize investment opportunities, making them more accessible to a broader audience.
Blockchain is reshaping industries with its potential for transparency, security, and decentralization, from finance to healthcare and beyond. While challenges like scalability and regulation remain, the opportunities for innovation are immense.
What do you think? Will blockchain drive the next wave of technological disruption? Share your thoughts in the comments!
For more insights on blockchain, Web3, and the future of decentralized tech, subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.